Introduction to Backhaul Network Technology
Backhaul network technology is the backbone of modern telecommunication systems. It connects core networks with access networks, enabling seamless data transfer between end users and service providers. Every call, video, or IoT transmission depends on the reliability of this intermediate layer. Without an efficient backhaul, even the most advanced access technologies like 5G or fiber-to-the-home cannot perform effectively.
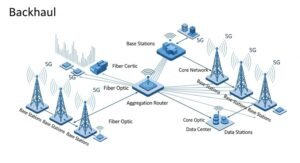
In telecom infrastructure, the backhaul serves as the bridge that carries aggregated traffic from distributed cell sites, base stations, or access points to the central core network. These links can be wired or wireless, depending on network design, capacity requirements, and geographical constraints.
Backhaul networks play a critical role in maintaining high throughput, low latency, and service quality. With the rise of 5G, edge computing, and massive IoT, the demand for advanced backhaul technologies has grown significantly. Service providers are upgrading legacy systems to fiber-based and millimeter-wave backhaul to meet these capacity and latency demands.
Understanding the Core Functionality
The core functionality of a backhaul network lies in transporting data between network nodes efficiently. It connects the radio access network (RAN) with the core network, ensuring stable data delivery.
There are two main types:
- Wired backhaul: Utilizes fiber optics, Ethernet, or microwave links. Offers higher reliability and bandwidth.
- Wireless backhaul: Relies on radio links, microwave, or satellite communication. Useful in remote or dense urban areas where physical cabling is costly.
Modern networks often deploy hybrid backhaul systems that combine both wired and wireless components to optimize performance, cost, and scalability.
Network operators design these systems based on capacity planning, redundancy, and scalability metrics to prevent congestion and ensure continuity during peak usage.
Components and Architecture of Backhaul Networks
A backhaul network consists of several interconnected components:
- Base Stations (BTS or eNodeB): Collect and transmit user data to aggregation nodes.
- Aggregation Nodes: Combine traffic from multiple cell sites for transmission to the core.
- Transport Links: Fiber, microwave, or satellite systems that carry data between nodes.
- Routers and Switches: Manage routing, quality of service (QoS), and load balancing.
The architecture can be point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, or mesh-based, depending on coverage requirements and topology. Mesh backhaul architectures are increasingly adopted for dense 5G networks and smart city deployments because they provide redundancy and dynamic routing capabilities.
Backhaul Technologies in Use
Key technologies shaping modern backhaul networks include:
- Fiber Optic Backhaul: Preferred for high-capacity transport. Offers scalability and minimal latency, making it ideal for 5G and enterprise networks.
- Microwave Backhaul: Used where fiber deployment is impractical. Supports high-capacity links with adaptive modulation.
- Millimeter-Wave Backhaul: Essential for 5G small cells, providing multi-gigabit throughput at short distances.
- Satellite Backhaul: Useful for remote or rural regions with limited terrestrial infrastructure.
- Ethernet and IP/MPLS: Provide flexible, packet-based transport and support for QoS mechanisms.
Each technology serves specific network conditions, and operators often use a combination to balance performance, cost, and coverage.
Role of Backhaul in 5G and IoT
The rollout of 5G networks has transformed backhaul requirements. Unlike previous generations, 5G demands ultra-low latency and higher bandwidth for applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart grids, and real-time analytics.
Backhaul must now handle:
- Massive device connectivity in IoT ecosystems
- Ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC)
- Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)
- Network slicing for differentiated service delivery
To meet these challenges, operators are deploying fiber-based and mmWave backhaul solutions integrated with software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV). These technologies allow dynamic bandwidth allocation and efficient traffic management.
Advantages of an Efficient Backhaul System
An optimized backhaul network delivers multiple benefits:
- Low Latency: Faster data transmission across network layers.
- High Throughput: Supports large-scale data traffic and multimedia streaming.
- Scalability: Adapts easily to network expansion.
- Reliability: Redundant design reduces downtime.
- Cost Efficiency: Hybrid approaches minimize deployment costs while maintaining performance.
These benefits directly impact user experience, operational efficiency, and service provider competitiveness.
Challenges in Backhaul Network Implementation
Despite its importance, deploying and maintaining backhaul infrastructure comes with challenges:
- High Deployment Costs: Especially for fiber installation in rural or dense urban zones.
- Spectrum Limitations: Wireless backhaul faces congestion and interference issues.
- Power and Environmental Constraints: Remote sites often lack stable power sources.
- Complex Network Management: Hybrid systems require advanced monitoring and optimization tools.
Operators address these issues through intelligent routing, spectrum reuse, and automation tools powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning.
The Future of Backhaul Networks
The future of backhaul technology is shifting toward intelligent, software-driven systems. As networks evolve to 6G, the focus will move to AI-based optimization, terahertz spectrum, and quantum-safe encryption for secure data transport.
Emerging trends include:
- Edge computing integration
- AI-powered predictive analytics
- Dynamic bandwidth management
- Energy-efficient backhaul solutions
These advancements will enable smarter, greener, and faster networks that can sustain the next generation of digital services.
Concolusion
Backhaul network technology is the hidden force behind digital connectivity. Its evolution determines how efficiently global communication systems operate. Investing in advanced, scalable backhaul infrastructure ensures high-quality user experiences, stable network operations, and readiness for future demands like 6G and massive IoT expansion.
If you want to learn more about the technology visit the techsslash.